Boot Auto-Start Configuration
After setting up the server environment, the project can run normally, but it needs to be started manually after shutdown. In some special scenarios, manual startup can be troublesome, so it is necessary to configure the project for auto-start. This tutorial mainly introduces the configuration of intranet penetration and project auto-start.
I. Configure Intranet Penetration
Linux Installation Method
- Manual Installation: Download the zip package suitable for the Linux platform from the official website, unzip it to get cpolar, and then run it with parameters through the command line.
- Automatic Installation: One-click automatic installation script
One-click Automatic Installation Script
Environmental Requirements:
This script is applicable to Ubuntu 16.04/18.04/20.04 and later, Centos 7/8 and later versions, the latest official Raspberry Pi image, and modern Linux operating systems that support systemd. The script will automatically detect the CPU architecture (i386/amd64/mips/arm/arm64, etc.), download the corresponding cpolar client, and deploy the installation automatically.
1. cpolar Installation (For Use in China)
curl -L https://www.cpolar.com/static/downloads/install-release-cpolar.sh | sudo bash
Or cpolar short link installation method: (For Use Outside China)
curl -sL https://git.io/cpolar | sudo bash
2. Check Version Number, Display 3.2.88.22
cpolar version
3. Token Authentication
Log in to the backend, check your authentication token, and then paste the token in the command line
cpolar authtoken xxxxxxx
4. Simple Penetration Test
cpolar http 8080
Press ctrl+c to exit
5. Add Service to System
sudo systemctl enable cpolar
6. Start cpolar Service
sudo systemctl start cpolar
7. Check Service Status
sudo systemctl status cpolar
8. Log in to the Backend, Check Tunnel Online Status
https://dashboard.cpolar.com/status
9. Installation Complete
You can go to the Getting Started Guide to further understand the usage of cpolar.
Note: cpolar Uninstallation Method
curl -L https://www.cpolar.com/static/downloads/install-release-cpolar.sh | sudo bash -s -- --remove
Installation Notes:
- Default installation path for cpolar: /usr/local/bin/cpolar,
- The installation script will automatically configure the systemd service script, allowing for auto-start on boot.
- If it is the first installation, a simple sample configuration file will be created by default, setting up two sample tunnels, one for web and one for ssh.
- cpolar configuration file path: /usr/local/etc/cpolar/cpolar.yml
10. Configure cpolar.yml
authtoken: xxx
tunnels:
ssh:
proto: tcp
addr: "22"
remote_addr: 1.tcp.cpolar.cn:prot
region: cn_vip
ap:
proto: http
addr: "8080"
region: cn_vip
hostname: app.xiaozhuo.top
gateway:
proto: http
addr: "80"
region: cn_vip
hostname: dev.xiaozhuo.top
mysql:
proto: tcp
addr: "3306"
remote_addr: 2.tcp.vip.cpolar.cn:prot
region: cn_vip
~
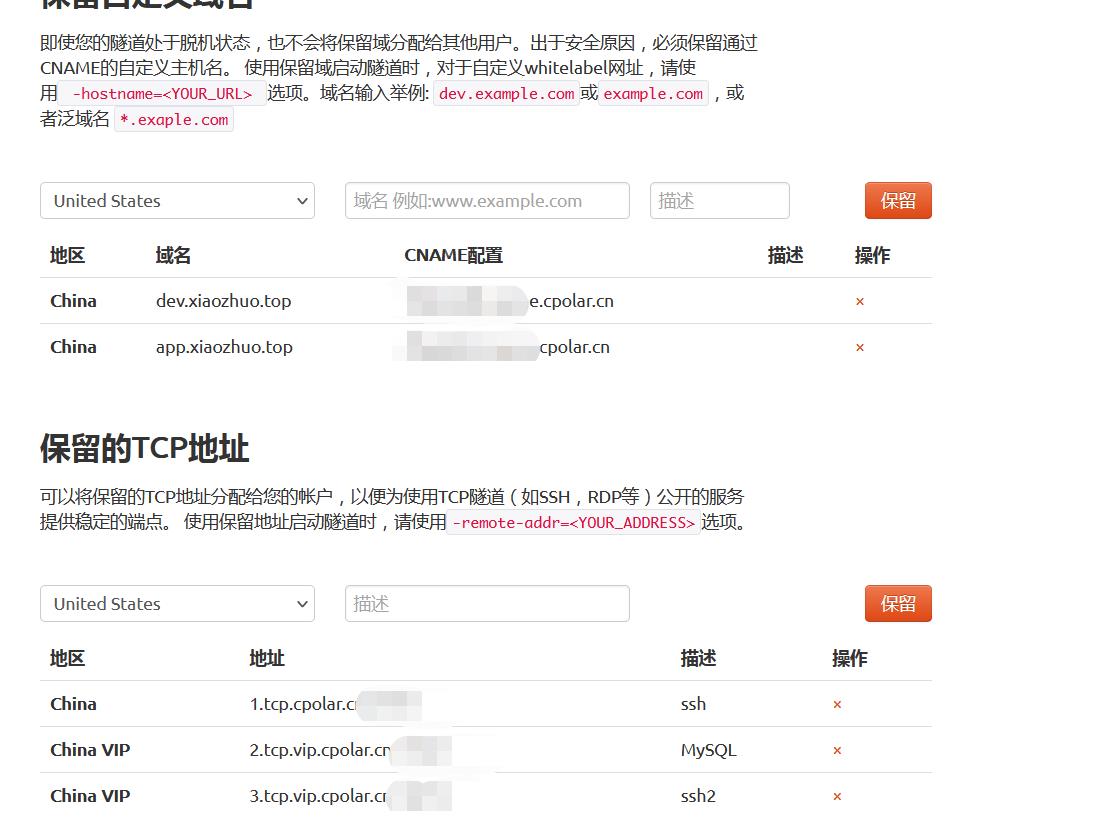
11. Backend Configuration of Domain Name and TCP Reserved Channel
II. Configure Startup Script
1. Write Manual Script
The manual script supports starting the project, stopping the project, checking the project status, restarting the project, and other functions
vim jeecg.sh
#!/bin/bash
#Replace this with your own executable, no other code changes needed
APP_NAME=jeecg-boot-module-system-3.1.0.jar
APP_PATH=/home/whut/ap/jeecg-boot-module-system-3.1.0.jar
#Usage instructions, used to prompt input parameters
usage() {
echo "Usage: sh script_name.sh [start|stop|restart|status]"
exit 1
}
#Check if the program is running
is_exist(){
pid=`ps -ef|grep $APP_NAME|grep -v grep|awk '{print $2}' `
#Return 1 if it does not exist, 0 if it does
if [ -z "${pid}" ]; then
return 1
else
return 0
fi
}
#Start method
start(){
is_exist
if [ $? -eq "0" ]; then
echo "${APP_NAME} is already running. pid=${pid} ."
else
nohup java -jar $APP_PATH 2>&1 &
echo "${APP_NAME} start success"
fi
}
#Stop method
stop(){
is_exist
if [ $? -eq "0" ]; then
kill -9 $pid
else
echo "${APP_NAME} is not running"
fi
}
#Output running status
status(){
is_exist
if [ $? -eq "0" ]; then
echo "${APP_NAME} is running. Pid is ${pid}"
else
echo "${APP_NAME} is NOT running."
fi
}
#Restart
restart(){
stop
start
}
#Select the corresponding method based on the input parameter, execute usage if no input
case "$1" in
"start")
start
;;
"stop")
stop
;;
"status")
status
;;
"restart")
restart
;;
*)
usage
;;
esac
2. Execute Manual Script
#Start project
sh jeecg.sh start
#Stop project
sh jeecg.sh stop
#Check project status
sh jeecg.sh status
#Restart project
sh jeecg.sh restart
3. Write Automatic Startup Script
vim /usr/local/sbin/start.sh
#!/bin/bash
#Project file storage path
APP_PATH=/home/whut/ap/jeecg-boot-module-system-3.1.0.jar
#File name
APP_NAME=jeecg-boot-module-system-3.1.0.jar
#Query existing processes
pid=`ps -ef|grep $APP_NAME|grep -v grep|awk '{print $2}' `
#Need to rest for two seconds here, otherwise the pid is not assigned successfully
sleep 2
#Kill existing processes
if [ $pid ]; then
echo "${APP_NAME} is already running. pid=${pid} ."
kill -9 $pid
echo "${pid} process terminated successfully"
sleep 2
fi
#Start project
if test -e $APP_PATH
then
echo 'File exists, start deployment'
nohup java -jar $APP_PATH 2>&1 &
else
echo '$APP_NAME file does not exist'
fi
#Start nginx after the project starts successfully, directly setting nginx to start on boot will result in an error due to the proxy domain not responding
sleep 60
service nginx start
4. Register Boot Startup Service
#Switch to system directory
cd /etc/systemd/system
#Edit and register service script
vim data.service
Edit content reference
[Unit]
Description=data server
# Dependencies, start after these programs
After=NetworkManager.service mysqld.service
[Service]
Type=forking
# Configure startup script
ExecStart=/usr/local/sbin/start.sh
# Configure restart script
ExecReload=/usr/local/sbin/restart.sh
# Configure stop script
ExecStop=/usr/local/sbin/stop.sh
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Continue to register boot startup
#Configure boot startup
systemctl enable data.service
#Reload configuration
systemctl daemon-reload
#Check startup configuration
systemctl list-unit-files | grep data
#Start service using systemctl
systemctl start data.service
#Stop service using systemctl
systemctl stop data.service