Common Git Commands
Projects often use Git to manage files and code, and there are many Git management tools available. This article aims to provide beginners with some simple tutorials to help them quickly become familiar with Git usage methods.
Introduction to Git
To understand Git, you first need to understand the following scenarios:
- Workspace: The current working area, where modifications start.
- Staging: After modifications, changes are added to the staging area, preparing them for commit.
- Local Repository: The local code repository, where changes are stored and only affect your local code. This is one of the differences from SVN; after an SVN commit, changes are directly submitted to the remote server, whereas after a Git commit, changes are only stored in the local repository.
- Remote Repository: The remote code repository, where you synchronize your local repository to share your work with other developers.
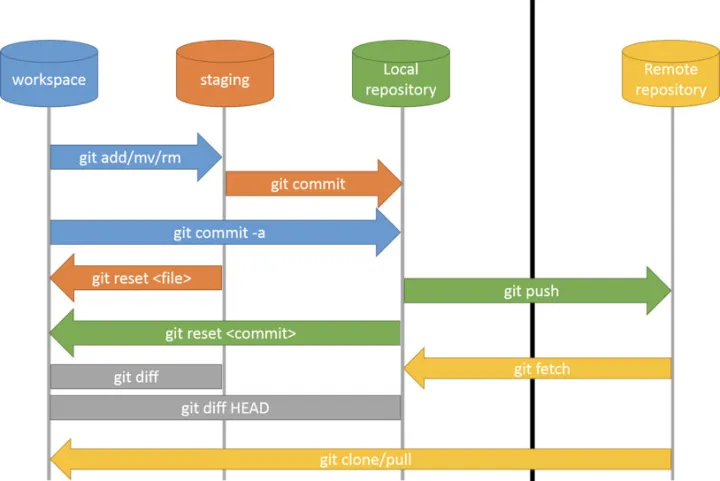
As shown in the diagram above, commands are used to interact between different scenarios. For example, git add submits files to the staging area, then git commit moves files from the staging area to the local repository, and git push sends them to the remote repository. The interactions described so far occur within a single branch, but Git also offers more powerful features, such as creating different branches that can be split and merged as needed.
Common Git Operations
Operations in Git Bash
- Open the project folder in your workspace, right-click, and select “Git Bash Here” to open the command input window.
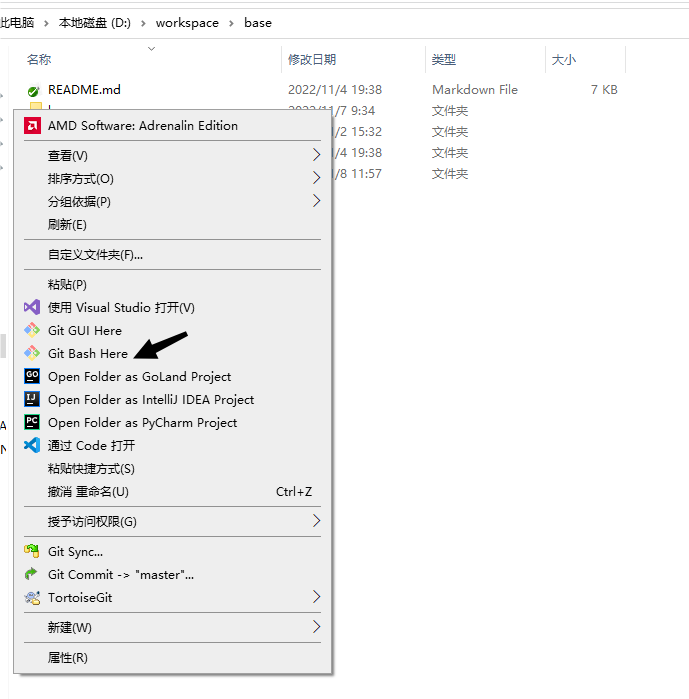
- Commit files to the remote repository
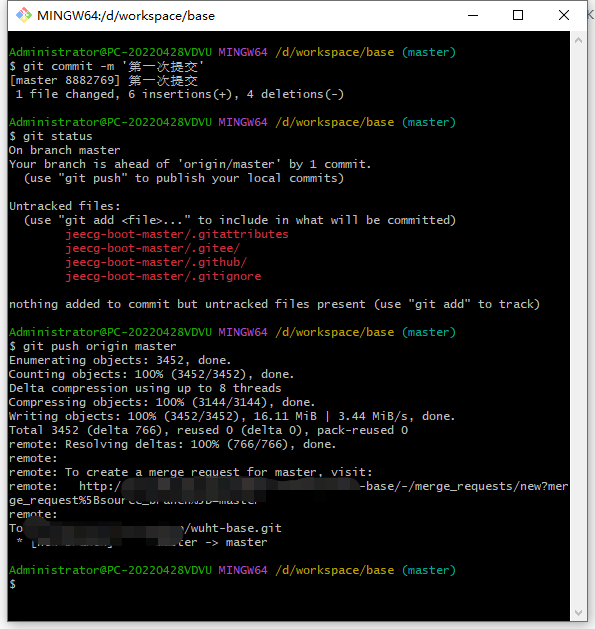
# Commit to local branch
git commit -m 'First commit'
# Check commit status
git status
# Push to remote branch
git push origin master
- Modify the remote repository URL
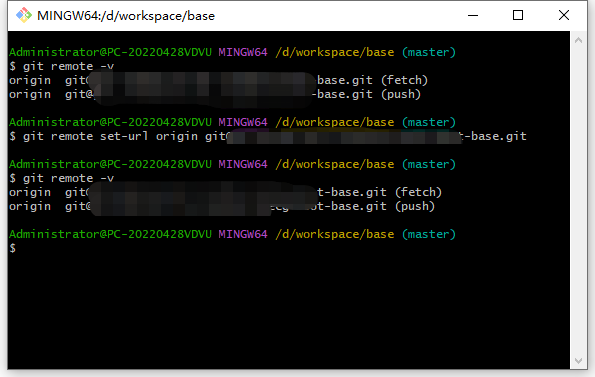
Administrator@PC-20220428VDVU MINGW64 /d/workspace/base (master)
$ git remote -v
origin git@git.xxx.com:xxx/xx-base.git (fetch)
origin git@git.xxx.com:xxx/xx-base.git (push)
Administrator@PC-20220428VDVU MINGW64 /d/workspace/base (master)
$ git remote set-url origin git.xxx2.com:xxx2/xx2-base.git
Administrator@PC-20220428VDVU MINGW64 /d/workspace/base (master)
$ git remote -v
origin git.xxx2.com:xxx2/xx2-base.git (fetch)
origin git.xxx2.com:xxx2/xx2-base.git (push)
Operations in TortoiseGit
- Open the project folder in your workspace, right-click, and select “TortoiseGit” to open the TortoiseGit submenu.
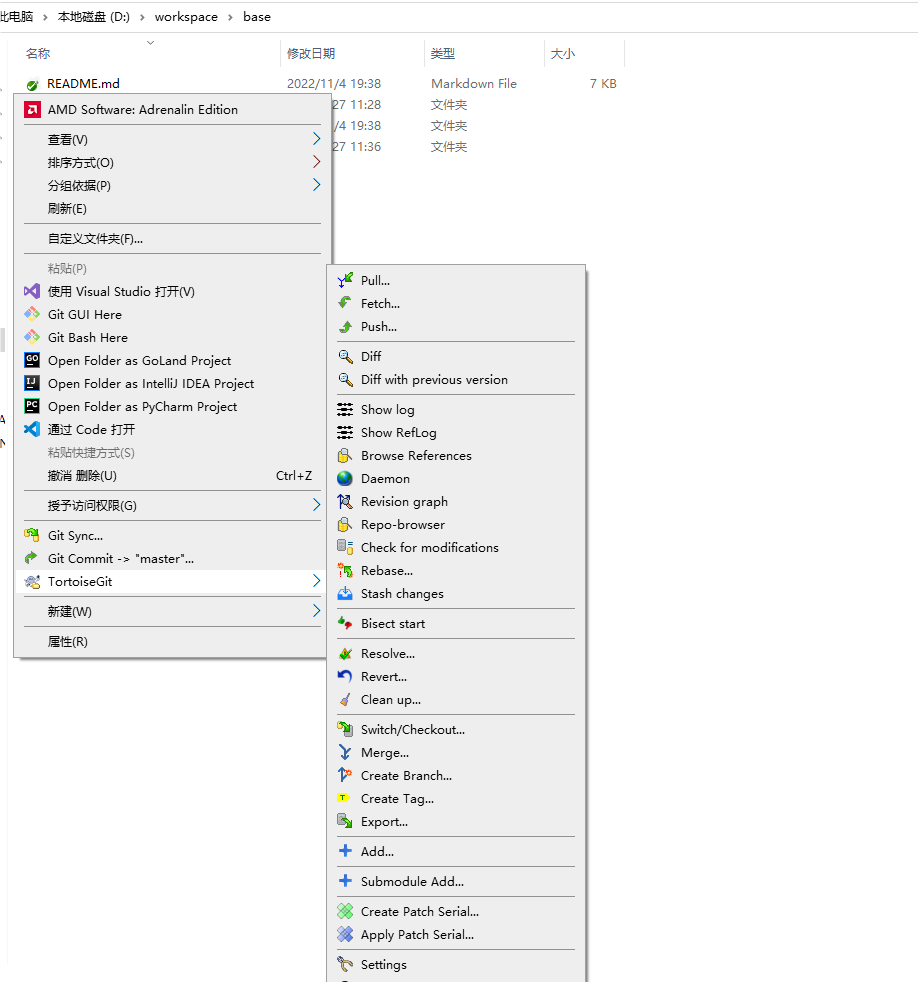
- Commit files to the remote repository
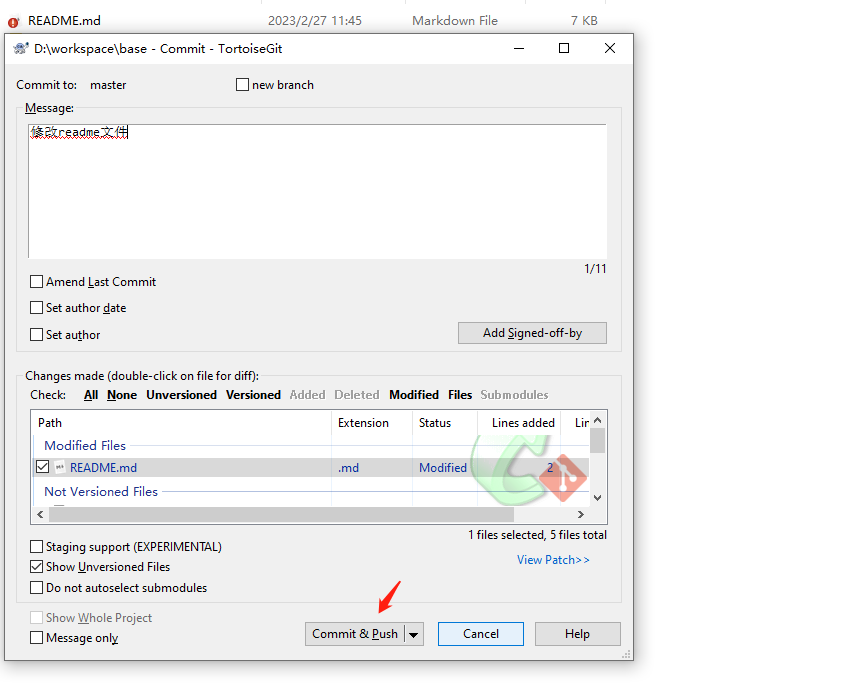
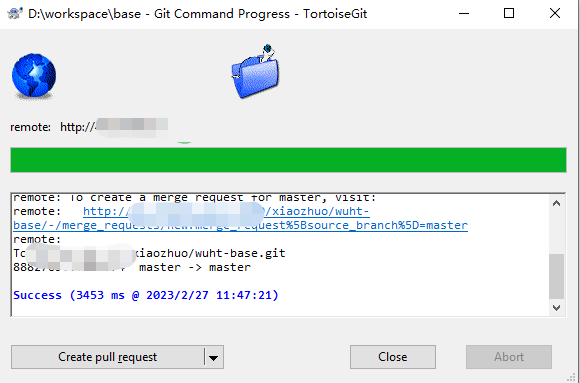
- Modify the remote repository URL
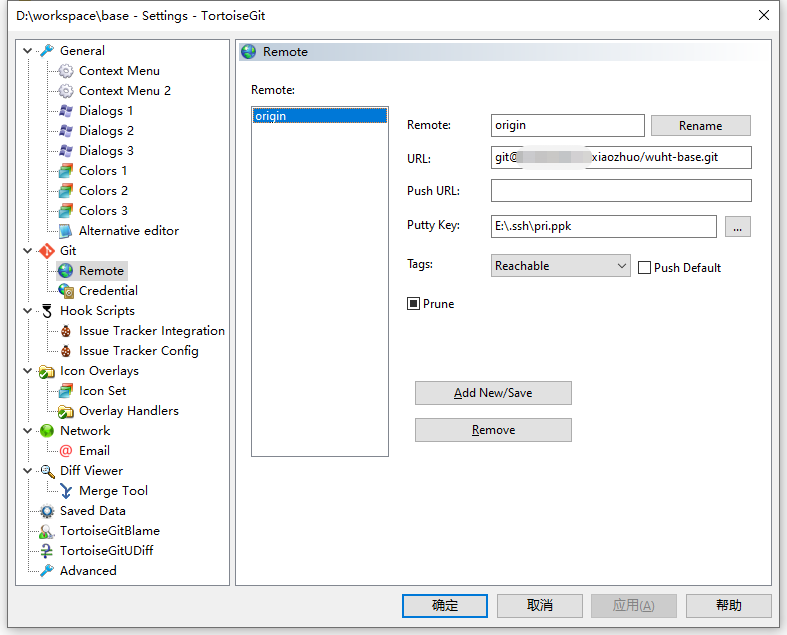
Operations in IDEA
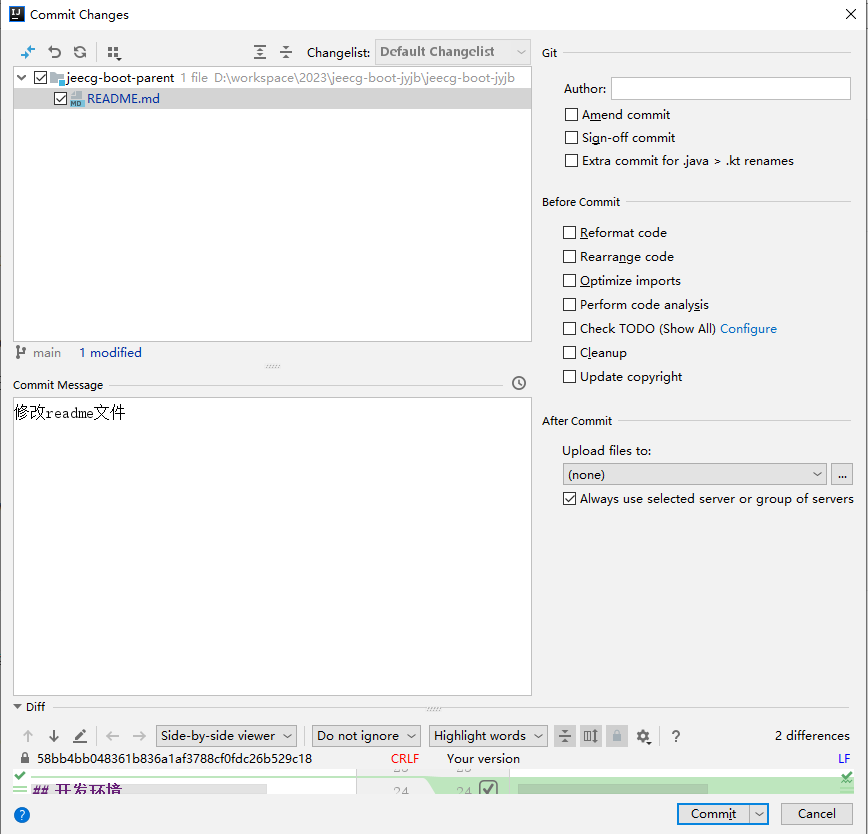
- Commit code to the remote repository
Click VCS—Git—Commit File to open the dialog box
Click VCS—Git—Push to open the dialog box
- Modify the remote repository URL
Click VCS—Git—Remotes to open the dialog box, select the repository URL, and click Edit
Полезный, вкусный и легкий салат, приготовление которого занимает считанные минуты. Сочные овощи способствуют тому, что семена чиа быстро набухают, поэтому долго ждать не придется. Просто подготовьте ингредиенты, смешайте и приступайте к трапезе
Blog
Можно сколько угодно рассуждать о том, что смузи – это всего лишь хайповый тренд. Но кроме того это еще и очень удобный и полезный перекус на скорую руку. И лично я уже не готова от них отказаться. Делюсь любимым рецептом тыквенного смузи
Сайт