COMTRADE Format Parsing
Introduction to COMTRADE Format
COMTRADE, short for COMmon format for Transient Data Exchange, is a standard format used for exchanging data from digital protection, control, and measurement equipment in power systems. The COMTRADE format is defined by the IEEE Std C37.111-1999 specification. It is a universal format supported by many manufacturers’ equipment. COMTRADE format files consist of a header file and a data file. The header file contains information about the data file, such as the sampling rate for each sample, the number of channels, data types, etc. The data file contains the sampled data for each channel, which can be voltage, current, signals, fault waveforms, etc. The COMTRADE format is very flexible and can adapt to various application scenarios. It can handle data from multiple channels simultaneously and supports both high-speed and low-speed sampling. Additionally, the COMTRADE format supports data compression and encryption to improve data transmission efficiency.
Detailed Explanation of COMTRADE Format
COMTRADE format files include a configuration file and a data file. The header file contains information about the data file, such as the sampling rate for each sample, the number of channels, data types, etc. The data file contains the sampled data for each channel, which can be voltage, current, signals, fault waveforms, etc.
The header file of the COMTRADE format includes the following information:
- File type: Determines whether the file is a configuration file (.cfg) or a data file (.dat).
- Station name: Identifies the name of the station.
- Number of channels: Determines the number of channels included in the data file.
- Sampling rate: The sampling rate for each channel in the data file, measured in Hertz.
- Number of samples: The number of samples for each channel in the data file.
- Timestamp: The start time and date of the data file.
- Data format: The data type for each sample in the data file (integer, floating point, etc.).
- Channel information: Information such as the name, unit, gain, etc., for each channel.
- Event information: Information about events (faults, switch operations, etc.) included in the data file.
The data file of the COMTRADE format includes the following information:
- Data file header: Header information of the data file, including information for each channel, event information, etc.
- Data records: Each record contains the sampled values for each channel at a specific time point.
The COMTRADE format has the following characteristics:
- Supports high-speed and low-speed sampling: The COMTRADE format can handle high-speed sampling data up to 1 million samples per second as well as low-speed sampling data.
- Supports multiple channels: The COMTRADE format can handle data from multiple channels, which can be voltage, current, signals, fault waveforms, etc.
- Supports data compression and encryption: The COMTRADE format supports various data compression and encryption algorithms to improve data transmission efficiency and security.
- Good compatibility: The COMTRADE format has been widely adopted, and many manufacturers’ equipment support this format.
- High flexibility: The COMTRADE format is very flexible and can adapt to various application scenarios.
# Station name, identifier number or name of the recording device, version year
110kVxx North Station,5635 Recorder,1999
# Total number of channels, number of analog channels, number of status channels
241,81A,160D
# Channel number, channel name, channel phase, monitored circuit element, channel unit, fCoefA[transformation factor A], fCoefB[transformation factor B], fTime[time offset], fMin[minimum value of this analog sample record data], fMax[maximum value of this analog sample record data], primary coefficient of the channel voltage or current transformer, secondary coefficient of the channel voltage or current transformer, P or S, indicating whether the value obtained from the channel conversion factor equation fCoefA * X + fCoefB is restored to a primary (P) or secondary (S) value
1,110kVⅠSection bus voltage Ua,A,110kVⅠSection bus voltage,V,0.0317994170,0.0000000000,0,-8191,8191,110000.0000000000,100.0000000000,S
2,110kVⅠSection bus voltage Ub,B,110kVⅠSection bus voltage,V,0.0317052193,0.0000000000,0,-8191,8191,110000.0000000000,100.0000000000,S
3,110kVⅠSection bus voltage Uc,C,110kVⅠSection bus voltage,V,0.0317111574,0.0000000000,0,-8191,8191,110000.0000000000,100.0000000000,S
...........
80,Plant distribution bus 700# cabinet current 3Io,N,Plant distribution bus 700# cabinet current,A,0.0353733636,0.0000000000,0,-8191,8191,2500.0000000000,5.0000000000,S
81,1-Frequency curve, , ,Hz,0.0050000000,0.0000000000,0,-8191,8191,1,1,S
# Channel number:1
# Channel name:110kVⅠSection bus voltage Ub
# Channel phase:A
# Monitored circuit element:110kVⅠSection bus voltage
# Channel unit:V
# fCoefA[transformation factor A]:0.0317994170
# fCoefB[transformation factor B]:0.0000000000
# fTime[time offset]:0
# fMin[minimum value of this analog sample record data]:-8191
# fMax[maximum value of this analog sample record data]:8191
# Primary coefficient of the channel voltage or current transformer:110000.0000000000
# Secondary coefficient of the channel voltage or current transformer:100.0000000000
# P or S, indicating whether the value obtained from the channel conversion factor equation fCoefA * X + fCoefB is restored to a primary (P) or secondary (S) value
# Where: The relationship between the actual value y and the sampled record data X: y = fCoefA * X + fCoefB
# Therefore, the actual extreme values: Min = fCoefA * fMin + fCoefB; Max = fCoefA * fMax + fCoefB;
# Switching quantities are: channel number/sequence number, channel name, channel phase, monitored circuit element, normal state of the status channel,
1,xx甲线 switch split position,NR,110kVxx甲线 current,0
2,xx乙线 switch split position,NR,110kVxx乙线 current,0
3,x高线 switch split position,NR,110kVx高线 current,0
.......
159,159# switching quantity channel,NR, ,0
160,160# switching quantity channel,NR, ,0
50 # System current voltage frequency is 50Hz
2 # There are two sampling frequencies
5000,5501 # First sampling frequency: 5501 points sampled at a sampling rate of 5000Hz
1000,8501 # Second sampling frequency: 8501 points sampled at a sampling rate of 1000Hz
15/10/2021,11:46:49.338900 # Sampling start time
15/10/2021,11:46:49.438900 # Sampling end time
BINARY # dat file recording format is BINARY (binary format), another format is ASCII
100 # Time scale factor
Python Processing of COMTRADE Format
Using Python to process waveform data can better view the status of the data and perform analysis. Below are some simple Python codes for processing COMTRADE files:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from comtrade import Comtrade
cfgFile = "/abcd.cfg"
datFile = "/abcd.dat"
rec = Comtrade()
rec.load(cfgFile, datFile)
# Number of analog channels
analog_count = rec.analog_count
# Loop to get the names of analog channels
for i in range(analog_count):
print(rec.analog_channel_ids[i])
# Number of digital channels
digital_count = rec.digital_count
# Loop to get the names of digital channels
for i in range(digital_count):
print(rec.digital_channel_ids[i])
# Loop to output the sampled data of 81 analog channels
for analog in rec.analog:
print(analog)
# Print the sampling time
print(rec.time)
# Print the sampling timestamp
print(rec.start_timestamp)
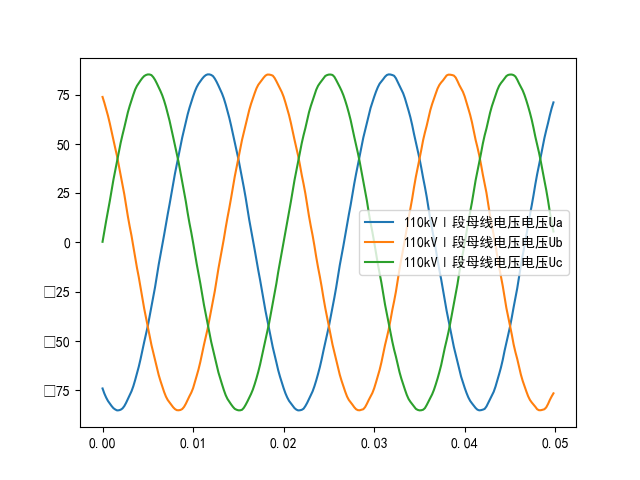
# Process the waveform data of the first three channels, only taking the first 250 points of sampled data due to the large amount of data
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'SimHei'
plt.figure()
plt.plot(rec.time[0:250], rec.analog[0][0:250])
plt.plot(rec.time[0:250], rec.analog[1][0:250])
plt.plot(rec.time[0:250], rec.analog[2][0:250])
plt.legend([rec.analog_channel_ids[0], rec.analog_channel_ids[1], rec.analog_channel_ids[2]])
plt.show()
Example of processed image
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.