Introduction
Recently, I completed a relatively complex calculation function in a project. The core idea is to add custom annotations to calculation classes, scan these annotations to identify the classes that need calculation, and then use multithreading and dynamic proxy to execute the calculation methods of these classes. Below is a simplified version of the code for your reference.
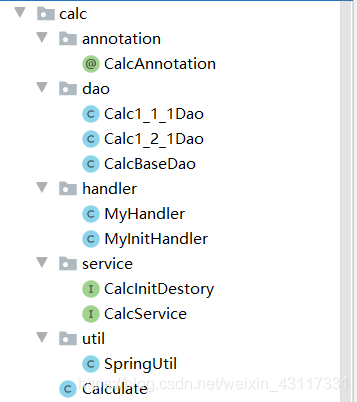
1. Package Structure
2. Custom Calculation Annotation
Create a custom annotation CalcAnnotation and scan classes with this annotation to execute their calculation methods.
/**
* Custom calculation annotation
* Adding this annotation indicates that the DAO needs calculation
*/
@Component
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface CalcAnnotation {
String name() default "";
}
3. Adding Calculation Classes
Create a class Calc1_1_1Dao that can perform its own calculation logic. Multiple such classes can be created based on requirements.
/**
* Calculation table 1-1-1
*/
@CalcAnnotation(name = "1-1-1")
public class Calc1_1_1Dao extends CalcBaseDao {
@Override
public void calculate() {
/*
Simulated calculation method
*/
List<String> list = super.calcCacheMap.get(super.almId);
list.add(year + " year " + month + " month calculation result of table 1-1-1");
calcCacheMap.put(almId, list);
System.out.println(year + " year " + month + " month execution of table 1-1-1 calculation completed");
}
}
4. Adding Calculation Base Class
This class implements the calculation interface and the initialization interface, and overrides some of their methods.
public class CalcBaseDao implements CalcService, CalcInitDestory {
/**
* Cache table calculation data
*/
public static Map<String, List<String>> calcCacheMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* Calculation input: year
*/
public static String year;
/**
* Calculation input: month
*/
public static String month;
/**
* Calculation ID: used to query calculation results
*/
public static String almId;
@Override
public void init() {
/*
Initialize a random calculation ID, initialize cache table
*/
System.out.println("Execute the initialization method of calculation baseDao");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
this.almId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
calcCacheMap.put(this.almId, list);
}
@Override
public void destory() {
System.out.println("Execute the destruction method of calculation");
}
@Override
public void calculate() {
}
@Override
public List<String> queryData(String almId) {
System.out.println("Execute the query method to query calculation results");
return calcCacheMap.get(almId);
}
@Override
public void setCalcParameter(Map<String, Object> parameter) {
if (parameter != null) {
this.year = getString(parameter.get("year"));
this.month = getString(parameter.get("month"));
}
}
@Override
public String getAlmId() {
return almId;
}
/**
* A utility method, can be written as a static method in a utility class
* @param obj
* @return String
*/
String getString(Object obj) {
if (null == obj || "".equals(obj) || obj.toString().startsWith("null")) {
return "";
} else {
return obj.toString().trim();
}
}
}
5. Creating Calculation Interfaces and Initialization Interfaces
Create a calculation interface
/**
* Calculation interface
*/
public interface CalcService {
/**
* Execute calculation
*/
void calculate();
/**
* Query calculation results
* @param almId Calculation ID
* @return
*/
List<String> queryData(String almId);
/**
* Set calculation parameters
* @param parameter
*/
void setCalcParameter(Map<String, Object> parameter);
/**
* Get calculation ID
* @return
*/
String getAlmId();
}
Create an initialization interface
/**
* Calculation initialization and destruction methods
*/
public interface CalcInitDestory {
void init();
void destory();
}
6. Creating Dynamic Proxy Handler Classes
Create a handler class for CalcService
/**
* Dynamic proxy handler, target class is CalcService
*/
public class MyHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private CalcService calcService;
public MyHandler(CalcService calcService) {
this.calcService = calcService;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Execute dynamic proxy interceptor method");
Object obj = method.invoke(calcService, args);
System.out.println("Execution of dynamic proxy interceptor method completed");
return obj;
}
}
Create a handler class for CalcInitDestory
/**
* Dynamic proxy handler, target class is CalcInitDestory
*/
public class MyInitHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private CalcInitDestory calcInitDestory;
public MyInitHandler(CalcInitDestory calcInitDestory) {
this.calcInitDestory = calcInitDestory;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Execute dynamic proxy method of initialization interface");
Object object = method.invoke(calcInitDestory, args);
System.out.println("Execution of dynamic proxy method of initialization interface completed");
return object;
}
}
7. Creating a Spring Container Utility Class
/**
* Springboot utility class
*/
@Component
public class SpringUtil implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
if (SpringUtil.applicationContext == null) {
SpringUtil.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
// Get applicationContext
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
// Get Bean by name
public static Object getBean(String name) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(name);
}
// Get Bean by class
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(clazz);
}
// Get specified Bean by name and class
public static <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> clazz) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(name, clazz);
}
// Get beans with annotation
public static Map<String, Object> getBeansWithAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> clazz) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = getApplicationContext();
Map<String, Object> map = applicationContext.getBeansWithAnnotation(clazz);
return map;
}
}
8. Creating the Core Calculation Class
The calculation class provides:
1. Pre-calculation method before(), to handle pre-calculation logic and determine if calculation can proceed.
2. Calculation method calculate(), which scans the Spring container for classes with the CalcAnnotation, then uses multithreading and dynamic proxy to execute their calculation methods.
3. Post-calculation method after(), to handle post-calculation logic such as shutting down the thread pool.
4. Query method queryData(String almId), to query calculation results by calculation ID.
/**
* Calculation class
*/
public class Calculate {
String year;
String month;
Map<String, Object> parameter = new HashMap<>();
/**
* Collection of calculation objects
*/
private List<CalcService> tables = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Multithreading calculation thread pool
*/
private ExecutorService pool;
public Calculate(String year, String month) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
parameter.put("year", year);
parameter.put("month", month);
}
public boolean before() {
/*
Dynamic proxy initialization method interface to execute initialization method
*/
CalcInitDestory proxy = (CalcInitDestory) Proxy.newProxyInstance(CalcInitDestory.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{CalcInitDestory.class}, new MyInitHandler(new CalcBaseDao()));
proxy.init();
/*
Pre-calculation logic: 1. Determine if calculation can proceed; 2. Initialize thread pool
*/
pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
return true;
}
public void after() {
/*
Post-calculation logic: Destroy thread pool
*/
pool.shutdown();
}
/**
* Execute calculation
* @return Calculation ID generated
*/
public String calculate() {
String almId = null;
try {
if (before()) {
List<Future<CalcService>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
addCalcService();
for (CalcService calcService : tables) {
/*
Start multithreading calculation
*/
futures.add(pool.submit(new Callable<CalcService>() {
@Override
public CalcService call() throws Exception {
// Dynamic proxy
System.out.println("Execute dynamic proxy method");
CalcService proxy = (CalcService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(CalcService.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{CalcService.class}, new MyHandler(calcService));
proxy.setCalcParameter(parameter);
proxy.calculate();
System.out.println("Dynamic proxy method execution completed");
return calcService;
}
}));
}
/*
Results of multithreading calculation
*/
for (Future<CalcService> future : futures) {
CalcService calcService = future.get();
System.out.println("Calculation ID in results: " + calcService.getAlmId());
almId = calcService.getAlmId();
List<String> queryData = calcService.queryData(calcService.getAlmId());
for (String str : queryData) {
System.out.println("Calculation result: " + str);
}
}
after();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return almId;
}
/**
* Get all `CalcService` by scanning Spring container for beans with `CalcAnnotation`
*/
private void addCalcService() {
Set<Map.Entry<String, Object>> entrySet = SpringUtil.getBeansWithAnnotation(CalcAnnotation.class).entrySet();
for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Object>> iterator = entrySet.iterator(); iterator.hasNext(); ) {
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = iterator.next();
CalcService calcService = (CalcService) entry.getValue();
tables.add(calcService);
}
}
/**
* Query calculation results
* @param almId Calculation ID
* @return Calculation results
*/
public List<String> queryData(String almId) {
CalcService proxy = (CalcService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(CalcService.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{CalcService.class}, new MyHandler(new CalcBaseDao()));
return proxy.queryData(almId);
}
}
9. Testing
@Test
void test() {
Calculate calculate = new Calculate("2020", "7");
String almId = calculate.calculate();
List<String> queryData = calculate.queryData(almId);
for (String str : queryData) {
System.out.println("Calculation result: " + str);
}
}
Test execution results

Some Remarks
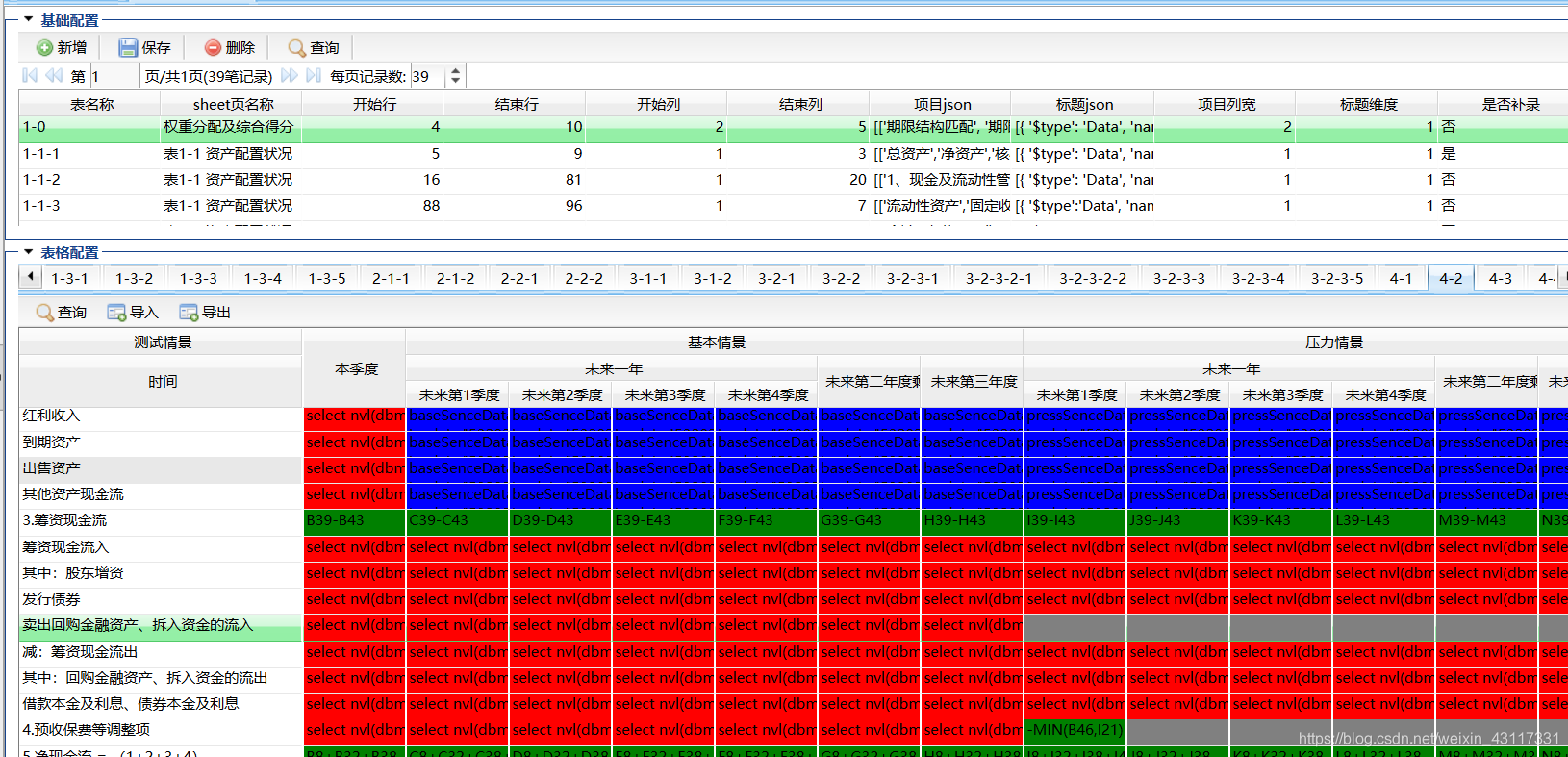
The above calculation is a simplified version of the calculation code. In actual business, I used calculation configurations to execute calculations. There are four types of calculation configurations:
1. Query data through SQL, as shown in the red part of the image.
2. Perform some calculations in the current calculation table like Excel formulas A1+B1, as shown in the green part.
3. Add method names and parameters in the calculation configuration, and add the calculation logic in the calculation class, as shown in the blue part.
4. Direct value passing, usually fixed values.