Initial Environment Setup for Ubuntu
This article mainly focuses on setting up the startup environment for jeecg-boot on a brand new Ubuntu system. The main software to be installed includes:
- JDK 8 and above
- Redis
- MySQL 5.7 or MariaDB 10.3
- Nginx
- SSH
- RXTX
After installing the environment, you also need to upload the backend jar package and the frontend dist folder, and then start the project.
1. Configure Mirror Sources
There are two ways to configure mirror sources: the common method is by modifying the configuration file, and the other is by configuring the mirror source through the desktop version’s “Software & Updates”.
1. Change Source by Modifying Configuration File
# Backup configuration file
sudo cp /etc/apt/sources.list /etc/apt/sources.list.bak
# Modify configuration file
sudo vi /etc/apt/sources.list
# Edit file and add mirror source
# USTC Mirror Source
deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# Tsinghua Mirror Source
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ impish-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
# Alibaba Mirror Source
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ impish main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ impish main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ impish-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ impish-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ impish-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ impish-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ impish-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ impish-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ impish-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ impish-backports main restricted universe multiverse
# 163 Mirror Source
deb http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ impish main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ impish main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ impish-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ impish-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ impish-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ impish-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ impish-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ impish-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ impish-backports main restricted universe multiverse
deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ impish-backports main restricted universe multiverse
Note: Change the system code to the current system code
# Refresh list and take effect
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
2. Modify Source Through Desktop Configuration
In Ubuntu 20.04.3 desktop version, click the “Show Applications” button in the bottom left corner, search for “Software & Updates”, and click to enter.
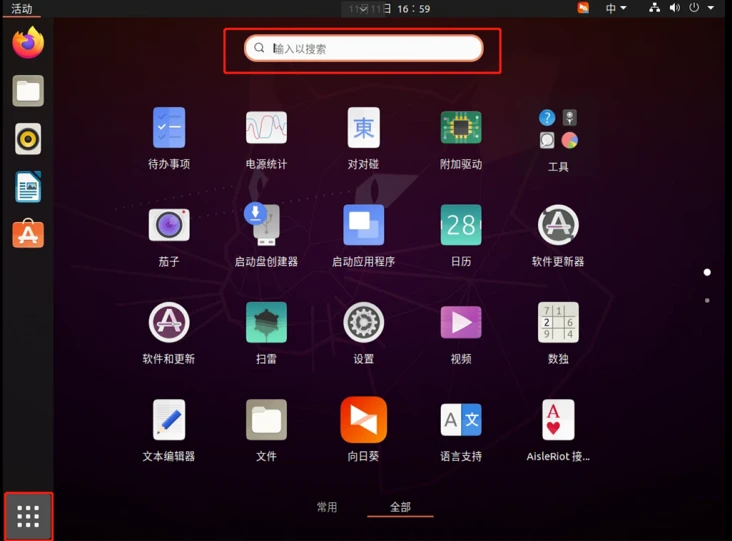
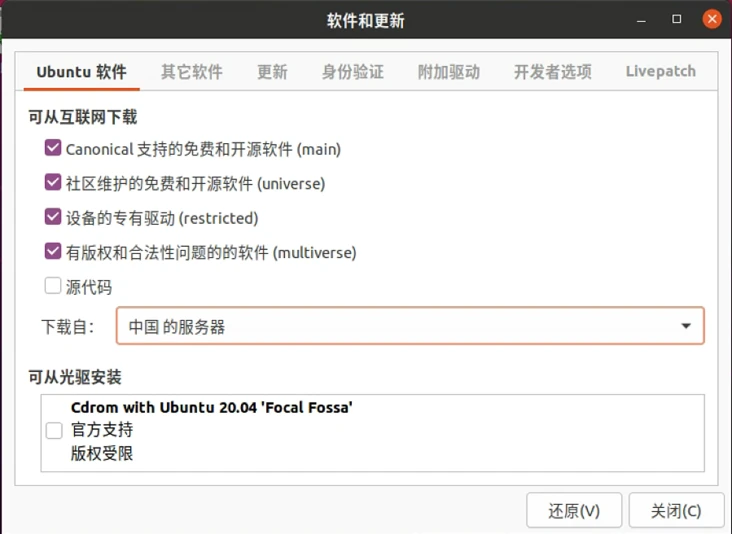
In the “Software & Updates” interface, under the “Ubuntu Software” section, select “Other Sites” from the “Download from” dropdown menu.
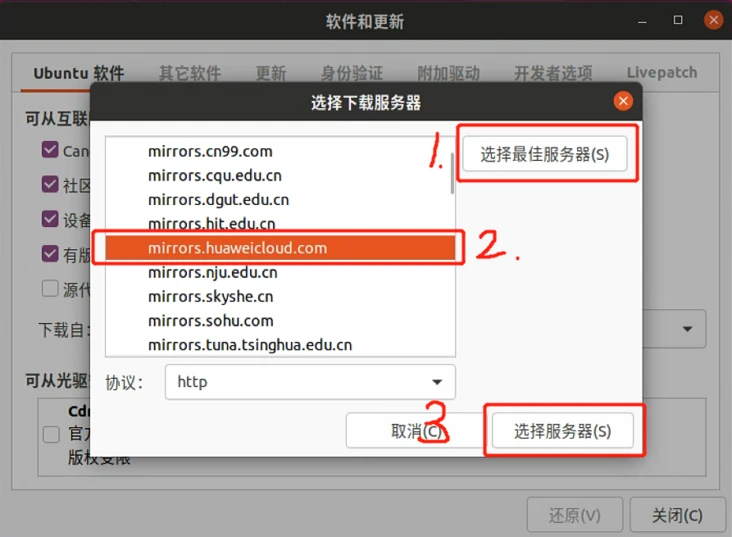
Then click “Select Best Server”, the system will automatically test the download servers, wait for a while, select the mirror server provided by the system, and the software source modification is complete.
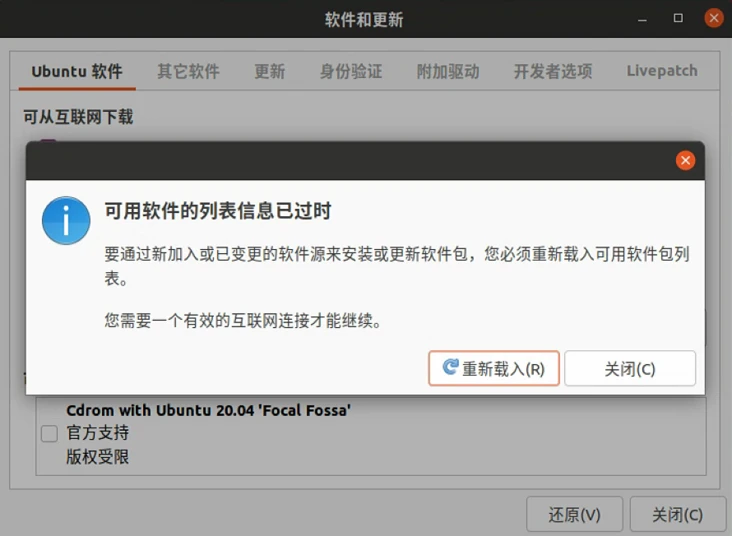
Close the “Software & Updates” interface, the system prompts “The list of available software information is outdated”, click “Reload” to update.
The above are the two methods to configure mirror sources.
Reference Blog: Two Methods to Change Ubuntu 20.04 Desktop Mirror Source
2. Install JDK
JDK can be installed online or locally. It is recommended to install online if there is network access, as it can be done through commands. Without network access, you can only install locally using a tar package. Here, only the online installation method is shown, installing JDK version openjdk-8.
# Find a suitable JDK version
sudo apt-cache search openjdk
Entering this command will yield many versions
openjdk-8-jdk - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK)
openjdk-8-jdk-headless - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) (headless)
openjdk-8-jre-headless - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT (headless)
openjdk-8-jre-zero - Alternative JVM for OpenJDK, using Zero/Shark
openjdk-8-source - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) source files
openjdk-11-jdk - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK)
openjdk-11-jdk-headless - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) (headless)
openjdk-11-jre-headless - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT (headless)
openjdk-11-source - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) source files
openjdk-13-jdk-headless - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) (headless)
openjdk-13-jre - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT
openjdk-13-jre-headless - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT (headless)
openjdk-13-jre-zero - Alternative JVM for OpenJDK, using Zero
openjdk-13-source - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) source files
openjdk-16-jdk - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK)
openjdk-16-jdk-headless - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) (headless)
openjdk-16-jre - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT
openjdk-16-jre-headless - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT (headless)
openjdk-16-jre-zero - Alternative JVM for OpenJDK, using Zero
openjdk-16-source - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) source files
openjdk-17-doc - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) documentation
openjdk-17-jdk - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK)
openjdk-17-jdk-headless - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) (headless)
openjdk-17-jre - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT
openjdk-17-jre-headless - OpenJDK Java runtime, using Hotspot JIT (headless)
openjdk-17-jre-zero - Alternative JVM for OpenJDK, using Zero
openjdk-17-source - OpenJDK Development Kit (JDK) source files
1. Install JDK
sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdk
2. Add Environment Variables
vim ~/.bashrc
# Add the following line at the end
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar
3. Verify Successful Installation
java -version
# If the following output appears, the installation is successful
openjdk version “1.8.0_91”
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_91-8u91-b14-0ubuntu4~15.10.1-b14)
OpenJDK Server VM (build 25.91-b14, mixed mode)
Reference Blogs:
Ubuntu JDK Installation Tutorial
3. Install MySQL
For some unknown reasons, MySQL mirrors are not found on all mirror sources now, suggesting the use of MariaDB instead. Therefore, the installation tutorial for MySQL is divided into two parts: installing MySQL and MariaDB. Choose one to install.
1.1. MySQL 5.7 Installation
# Check if MySQL is installed:
dpkg -l | grep mysql
# Install MySQL:
sudo apt install mysql-server
# Check if the installation is successful:
netstat -tap | grep mysql
# After checking with the above command, if you see mysql's socket in LISTEN state, it indicates successful installation.
1.2. MySQL Configuration After Installation
If you cannot log in directly, configure the database for passwordless login. If you can, skip this step.
# Stop MySQL service
sudo service mysql stop
# Modify MySQL login settings to temporarily disable password verification
sudo vim /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
# Comment out "skip-external-locking" under [mysqld]
# Add "skip-grant-tables" and save and exit
# Restart MySQL database
sudo service mysql start
1.3. Log in to the Database
# Log in to MySQL database without password
mysql -u root mysql
# Enter MySQL table space
use mysql;
# Modify root account password
update user set authentication_string=password("123456"),plugin='mysql_native_password' where user='root';
# Create a new user
create user 'jeecg'@'%' identified by '1qaz@WSX';
# Grant permissions to the user
grant all privileges on *.* to 'jeecg'@'%';
1.4. Modify Configuration File
# Modify configuration file
sudo vim /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf
# Add the following configurations
# Configure case-insensitive
lower_case_table_names = 1
# If passwordless login is configured, uncomment "skip-external-locking" under [mysqld]
# Modify binding IP as needed
change bind 127.0.0.1 to bind 0.0.0.0, allowing access from all IPs
# Restart MySQL after modifications
sudo service mysql restart
2.1. MariaDB 10.3 Installation
# Check if the database is installed:
dpkg -l | grep mysql
# Install MariaDB
sudo apt install mariadb-server-10.3
# Configure root account and connection permissions
sudo mysql_secure_installation
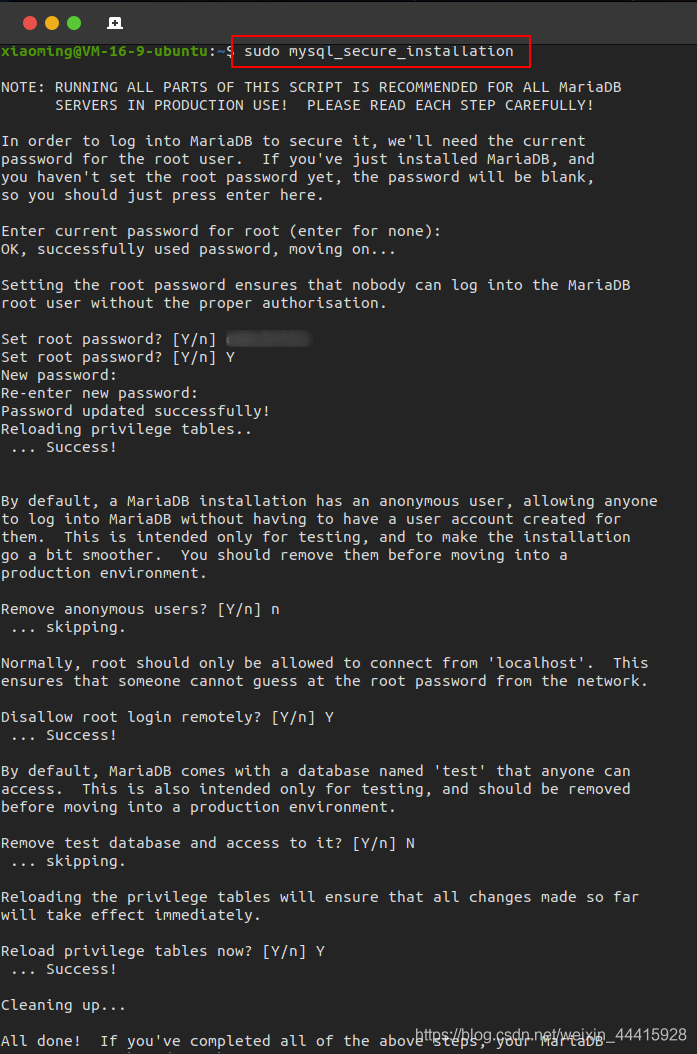
2.2. Check Database Running Status
sudo systemctl status mysql.service
2.3. Log in to Database and Create New User
# Log in
sudo mysql -u root -p
# Enter MySQL table space
use mysql;
# Create user
create user 'jeecg'@'%' identified by '1qaz@WSX';
# Grant permissions to the user
grant all privileges on *.* to 'jeecg'@'%';
2.4. Configure Database Configuration File
# Modify configuration file
sudo vi /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnf
# Add the following configurations
# Configure case-insensitive
lower_case_table_names = 1
# Modify binding IP as needed
change bind-address to 0.0.0.0
# Restart MySQL after modifications
sudo service mysql restart
Reference Blogs:
Ubuntu Install MariaDB 10.3 Database (Equivalent to MySQL 5.7)
4. Install Redis
1. Install Redis
# Install redis
sudo apt-get install redis-server
2. Edit Configuration File
sudo vi /etc/redis/redis.conf
# Add configuration - Add password
requirepass 123456
# Uncomment if external access is needed
bind 127.0.0.1 ::1
# Modify port
port 6379
3. Restart Redis to Apply Configuration
# Commonly used first method
sudo redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf
sudo /etc/init.d/redis-server restart
sudo service redis-server restart
5. Install Nginx
1. Execute Installation Command
sudo apt-get install nginx
2. Installation Directory
-
Downloaded software storage location: /var/cache/apt/archives
-
Default location after installation: /usr/share
-
Executable file location: /usr/bin
-
Configuration file location: /etc/nginx
-
lib file location: /usr/lib
3. Modify Configuration File
sudo vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Change the configuration to the following:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
gzip on;
gzip_min_length 1k;
gzip_comp_level 9;
gzip_types text/plain application/javascript application/x-javascript text/css application/xml text/javascript application/x-httpd-php image/jpeg image/gif image/png;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";
server {
listen 80;
server_name jeecg;
# Backend service configuration, enabling this location allows access via http://domain/jeecg-boot/xxxx
location ^~ /jeecg-boot {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/jeecg-boot/;
proxy_set_header Host 127.0.0.1;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
# Solve the problem of not finding the page when refreshing the route address in Router(mode: 'history')
location / {
root html/dist;
index index.html index.htm;
if (!-e $request_filename) {
rewrite ^(.*)$ /index.html?s=$1 last;
break;
}
}
}
}
4. Change Folder Permissions
Since the root directory in the configuration is html/dist, the full path is /usr/share/nginx/html. Place the compiled dist folder here. To upload files successfully, you must modify the permissions of the html folder.
sudo chmod 777 /usr/share/nginx/html