When developing a project, Java needs to call MATLAB algorithms to execute some computational logic. The conventional approach is to package MATLAB files into a JAR package, and the Java project references this JAR package for the call. However, in actual algorithms, some solvers are introduced, which cannot be called in the JAR package code, leading to calculation failures. This article mainly introduces how to package MATLAB files into an SDK and deploy them to a server in algorithm files with solvers, and call them through RESTful-style APIs.
1. Install MATLAB 2024a
Follow the WeChat official account [火耳软件安装], install step by step according to the tutorial, and after installation, you need to configure the MATLAB runtime environment, which can be directly added to the environment variables.
Find these two folders in the MATLAB installation path and add them to the path variable:
%matlab installation path%\bin
%matlab installation path%\runtime\win64
2. Install CPLEX Solver
Reference link: https://blog.csdn.net/wojianguile/article/details/135508587
3. Write MATLAB Algorithm Code and Java Test Code
Refer to the official documentation: https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/compiler_sdk/mps_dev_test/test-in-process.html
3.1 Write a MATLAB Algorithm Including CPLEX Solver
Write a simple MATLAB algorithm that includes the CPLEX solver
function b = calc(a)
% Define optimization variables
x = sdpvar(2, 1); % Create a 2x1 optimization variable vector
% Define optimization problem
Constraints = [x >= a]; % Add constraint: variable x is greater than or equal to a
Objective = x(1) + x(2); % Add objective function: minimize x(1) + x(2)
% Set optimization parameters
options = sdpsettings('verbose',2,'solver', 'cplex');
options.cplex.display='on';
% Solve optimization problem
sol = optimize(Constraints, Objective, options);
% Output results
if sol.problem == 0
disp('Optimal solution:');
disp(value(x)); % Output optimal solution
disp(['Optimal objective function value: ', num2str(value(Objective))]); % Output optimal objective function value
else
disp('Failed to find optimal solution.');
end
b = value(Objective);
end
3.2 Compile Algorithm File
Select Production Server Compiler in the APP
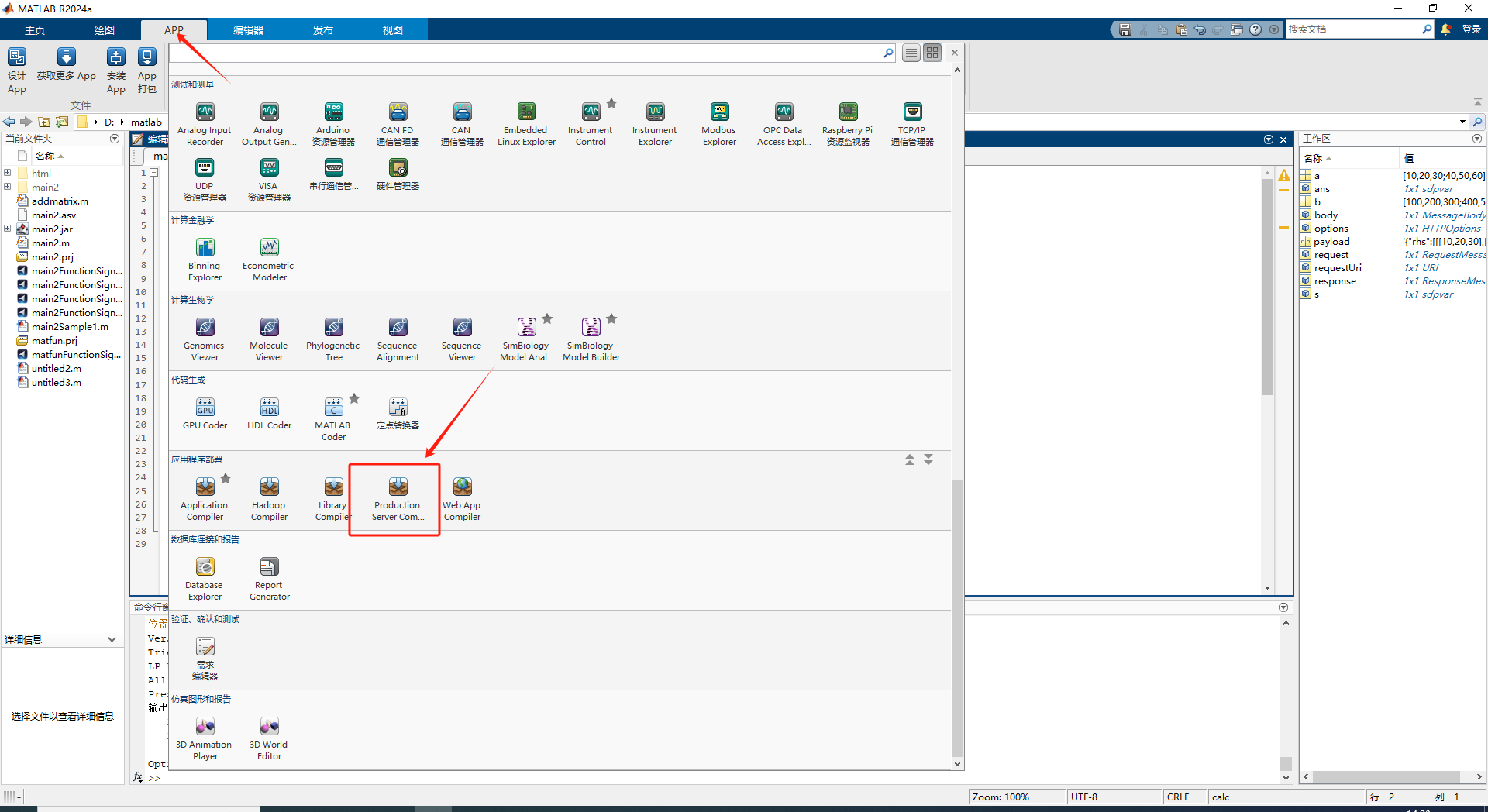
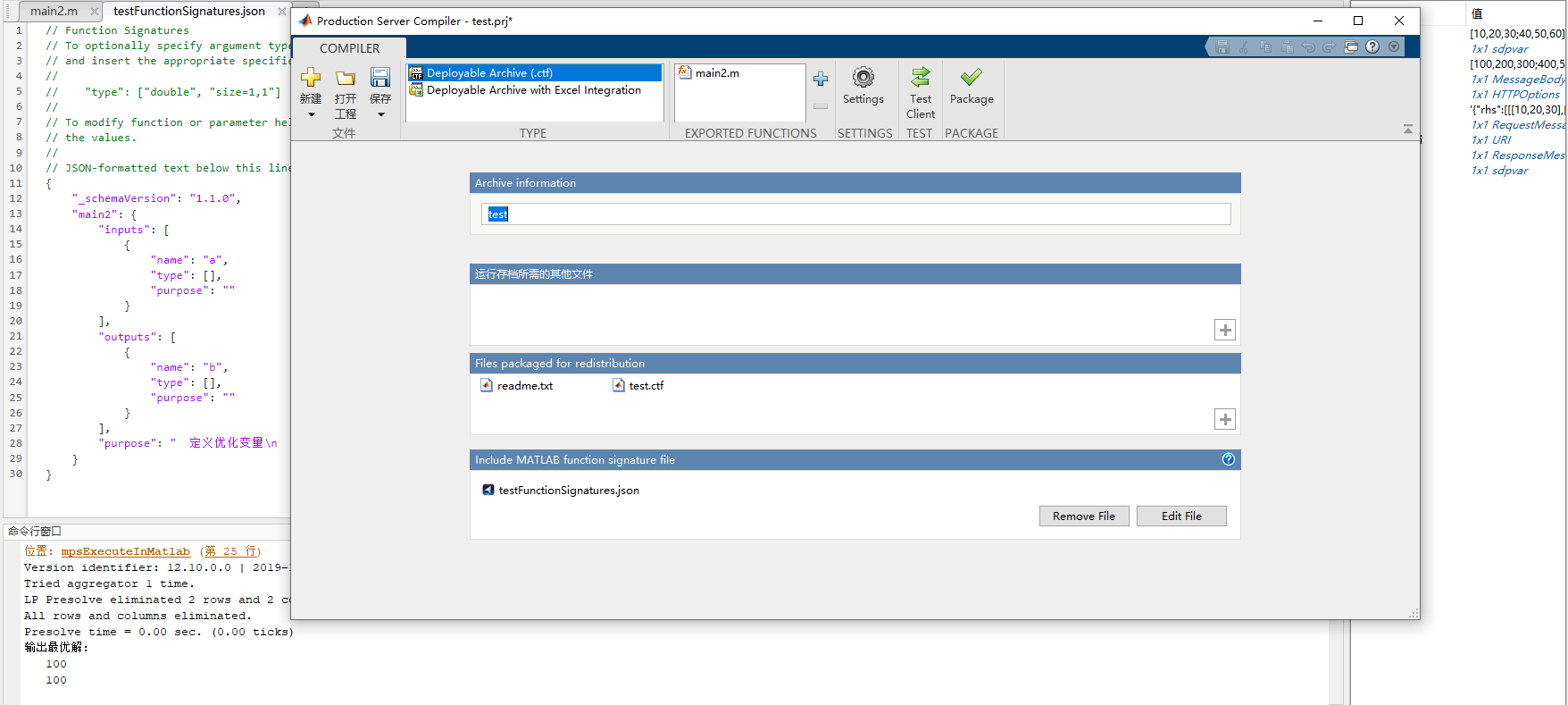
In the pop-up box, add the algorithm file you just wrote. You can choose to modify Archive information, which will be used as the root path of the API interface. You also need to Include MATLAB function signature file. Clicking the Create File button will automatically generate a JSON file, which does not need to be modified.
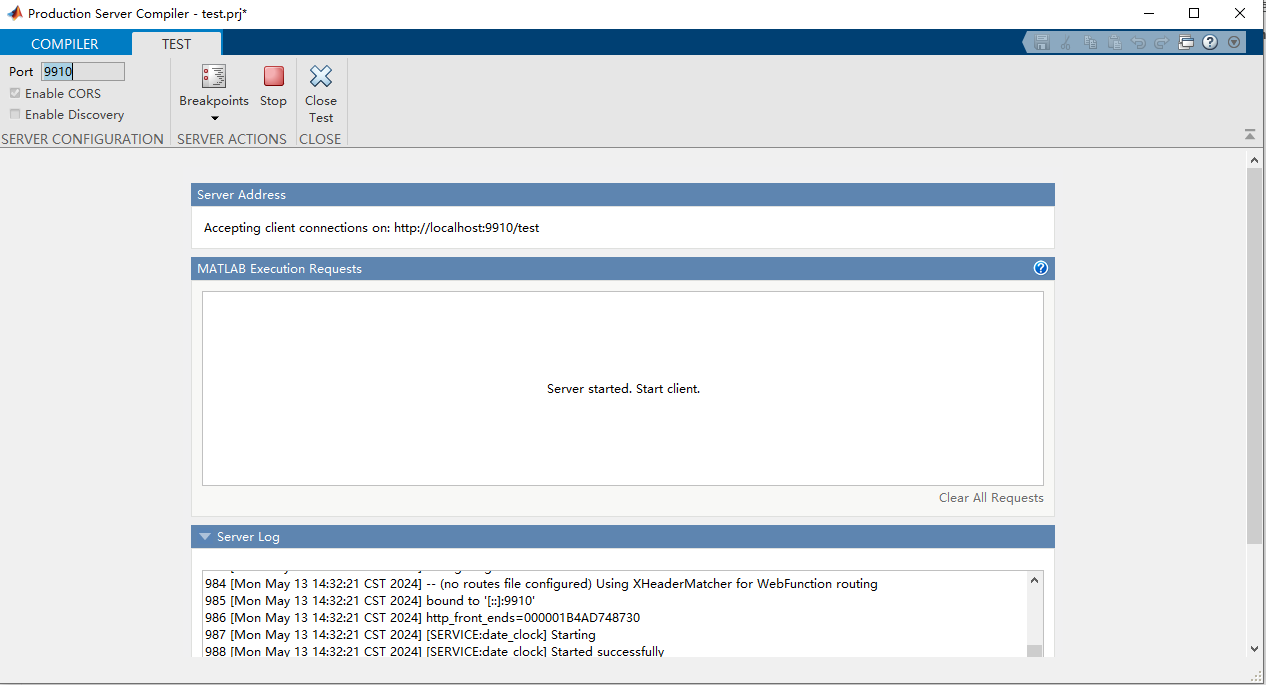
Open the test client, click Test Client, in the pop-up box, you need to check Enable CORS to support cross-domain requests, otherwise, it will cause the call to fail, then click Start.
3.3 Set Up Java Environment and Write Test Code
Set up the Java environment. When calling the test code, you need the mps_client.jar package and the javabuilder.jar package.
Find the mps_client.jar package and the javabuilder.jar package in the MATLAB installation path, the paths are as follows:
%matlab installation path%\toolbox\compiler_sdk\mps_clients\java\mps_client.jar
%matlab installation path%\toolbox\javabuilder\jar\javabuilder.jar
For Maven projects, you can add them through dependency references
mvn install:install-file -Dfile=E:\MATLAB2024\toolbox\javabuilder\jar\javabuilder.jar -DgroupId=com.mathworks.toolbox -DartifactId=javabuilder -Dversion=1.0.0 -Dpackaging=jar
mvn install:install-file -Dfile=E:\MATLAB2024\toolbox\compiler_sdk\mps_clients\java\mps_client.jar -DgroupId=com.mathworks.toolbox -DartifactId=mps_client -Dversion=1.0.0 -Dpackaging=jar
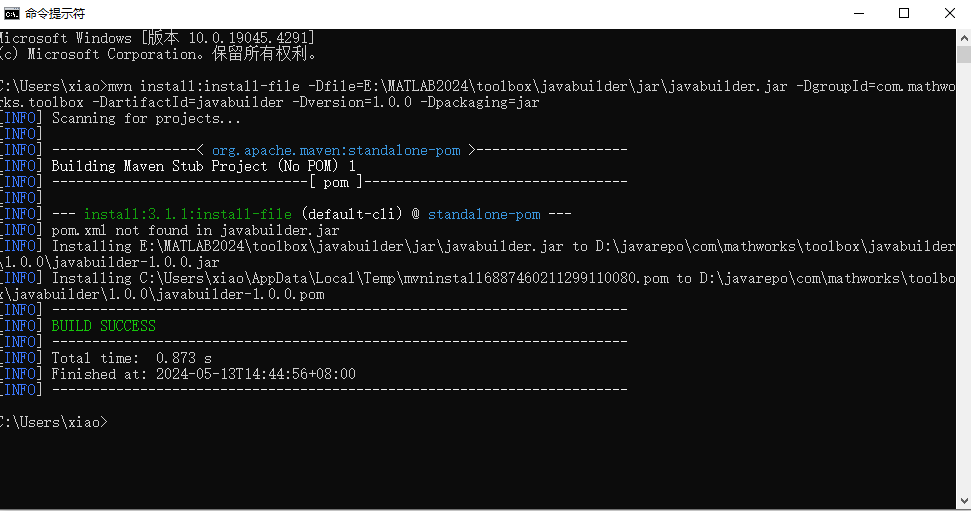
Add project dependencies in the pom file
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mathworks.toolbox</groupId>
<artifactId>javabuilder</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mathworks.toolbox</groupId>
<artifactId>mps_client</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
Write Java interface call test code
import com.mathworks.mps.client.MATLABException;
import com.mathworks.mps.client.MWClient;
import com.mathworks.mps.client.MWHttpClient;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
interface Main2Test
{
Object main2(double a1)
throws MATLABException, IOException;
}
public class Main2Example {
public static void main(String[] args){
double a1= 100;
MWClient client = new MWHttpClient();
try{
Main2Test m = client.createProxy(new URL("http://localhost:9910/test"),
Main2Test.class);
Object result = m.main2(a1);
System.out.println("Return result:"+result);
}catch(MATLABException ex){
// This exception represents errors in MATLAB
System.out.println(ex);
}catch(IOException ex){
// This exception represents network issues.
System.out.println(ex);
}finally{
client.close();
}
}
}
Test the execution result of the interface
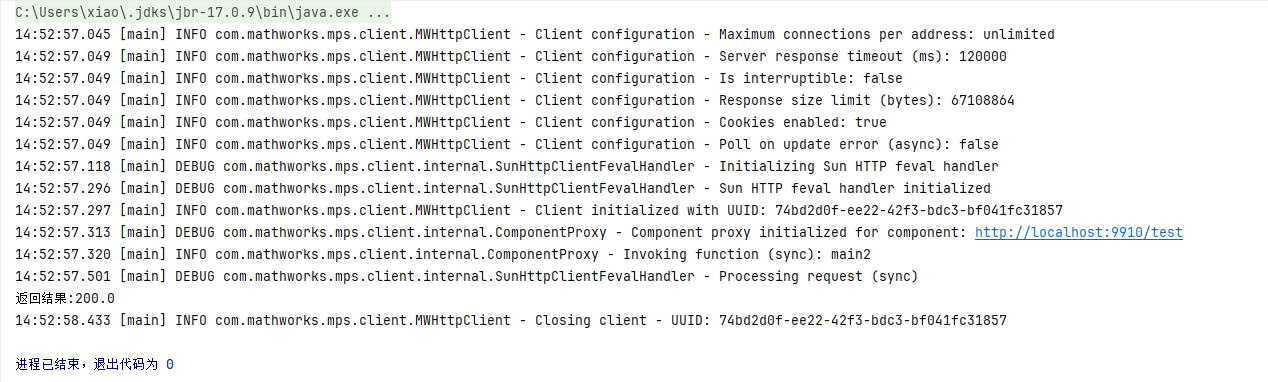
You can see the algorithm call information in both the MATLAB test client and the console
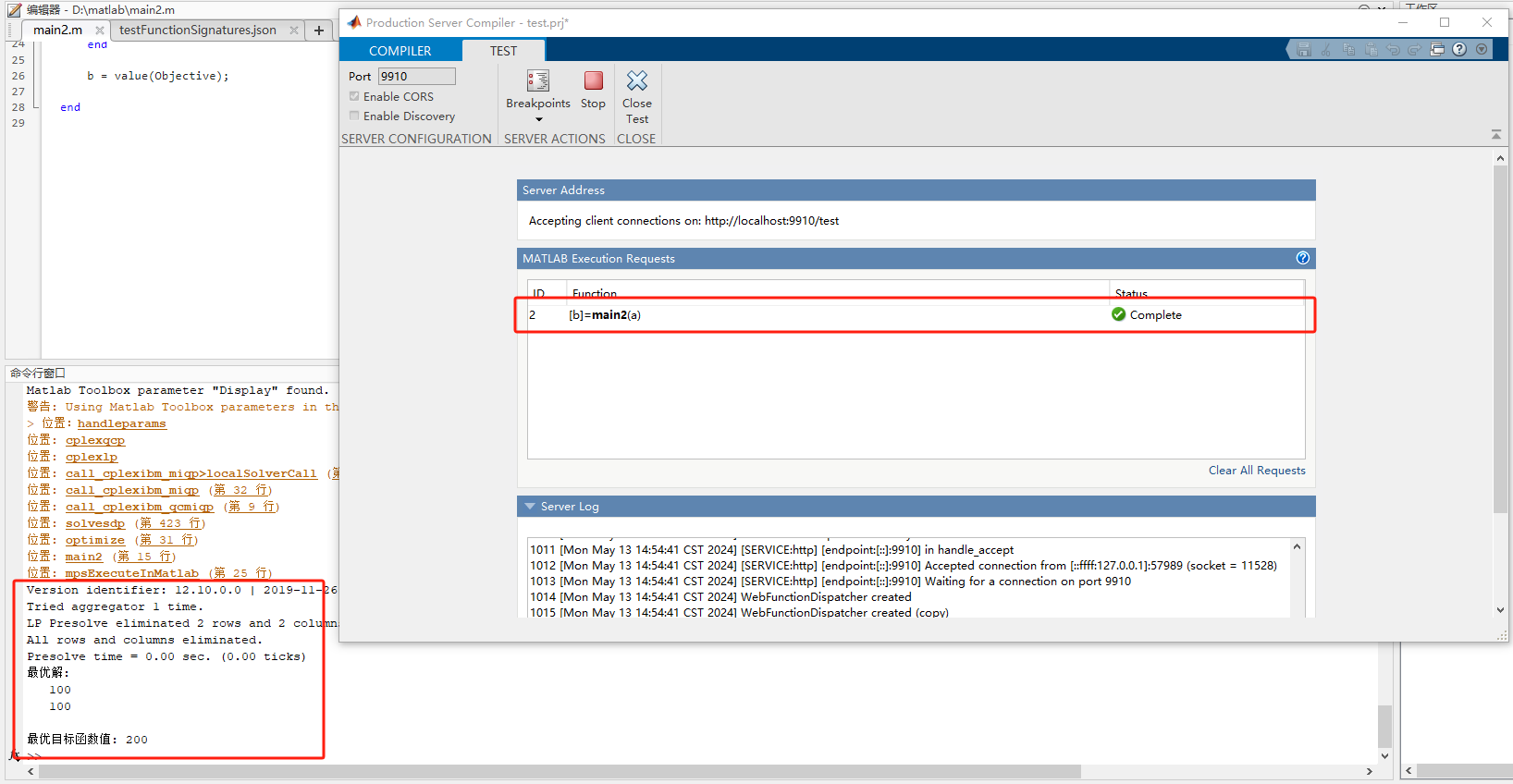
The above results indicate that the test has been completed. Package the project into a CFT file, click the Package button to package